Configure Drupal
Translate
Translation occurs at several levels. In Drupal 10, all translation modules are already in core and just have to be enabled. Start by enabling the Language module, then add at least another language.
- Content entity translation: enable the Content Translation module.
- Configuration entity translation (everything that lives in the YAML files) : enable the Configuration Translation module.
- User interface translation (everything that is defined by the
tfunction): enable the Interface Translation module.
The most probable use case is that you want to enable these 4 modules for a fully multilingual website.
A really valuable serie of blog posts is the translation tidbits serie from Gábor Hojtsy (opens in a new tab).
In a serie of 20 posts (opens in a new tab), he covers everything that you should know about the translation system
Here is the key link to configure your website: /admin/config/regional.
Get clean URLs based on patterns
Use the Pathauto (opens in a new tab) module.
Redirect URLs
To fix 404 or to handle automatic URL renaming, use the Redirect (opens in a new tab) module.
Choose between decimal or float
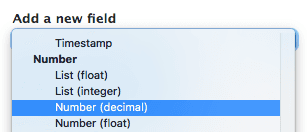
When adding a new field, you could have to answer this question for numbers.
This is pretty well explained in this article Decimal, Float or Integer in Drupal Fields? (opens in a new tab)
As a summary:
Float is definitely the most confusing of the number fields.
Here's our simple rule: if you don't know what a floating point number is, you don't need to use the Float field.
So, in most cases, just use Decimal.
Access control
Per entity access
The Content Access (opens in a new tab) module covers content access per content type with default values and the possibility to override them per content.
Also, have a look at the ACL (opens in a new tab) and Group (opens in a new tab) modules.
Per field access
The Field Permissions (opens in a new tab) module
Comparison and Overview of Access Control modules (opens in a new tab)
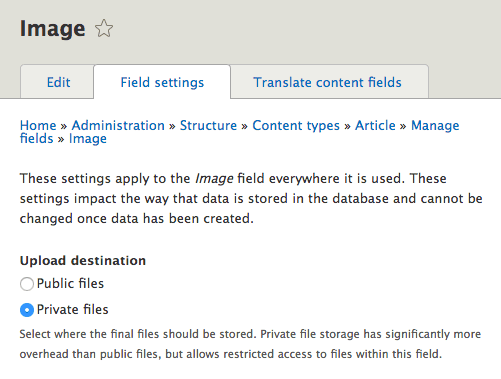
Private file system
This can be used for file and image fields and should be done prior to any content insertion for this field.
- Edit the sites/default/settings.php file, then uncomment and set this value, preferably outside of the docroot:
$settings['file_private_path'] = '/path/to/site/private-files'; - Cache rebuild
drush cr - Go to Configuration > Media > File System (/admin/config/media/file-system) and check the "Private local files served by Drupal." radio at the bottom of the page.
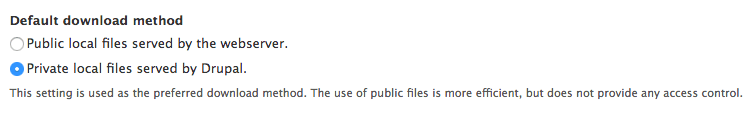
- Configure your field(s) per entity type (Node, User, ...) to use the private file system.
Share configuration between environments
See also the development section about configuration management.
Send mails reliably
The easiest configuration is to use a transactional email solution like Mailgun (opens in a new tab) (10,000 emails free every month), Sendgrid (opens in a new tab) or Mandrill (opens in a new tab).
Spam prevention
- If your website is not based on user registration, uncheck the Configuration > Account settings > Who can register accounts?
- Review if comments are open (they are by default on the Article content type).
- Install Spam control modules
Get backups
Use the Drupal Backup and Migrate (opens in a new tab) module if your hosting provider does not cover this case.
It allows to run scheduled or manual backups