Content modelling
Start with an MVP
Drupal is powerful and you can get fast a complex content model and features on top of that.
So it can be tempting to quickly deliver the full product. Instead of that, try to iterate and follow Agile principles (opens in a new tab) (SCRUM, Lean, ...).
Make a good plan
Creating content types, vocabularies and relations on the fly will lead to a cluttered user interface and unmaintainable data structure.
Here is a really simple methodology that can apply in most projects:
- Discuss the business rules with the product owner
- Discuss with the persons that will use Drupal as content editors
- Use what fits well to represent the content model: mind map (opens in a new tab), UML diagrams (opens in a new tab) (use case and sequence diagram for features and class diagram for the entities are more than enough, no need to use more here).
- Validate your model with real content
- Iterate, test and improve
Avoid to define too many content types
Be honest with the reality of the content editors, if the goal is to publish a few news and jobs a year, do not create two separate content types, the default Article content type with a reference to a vocabulary Article type with jobs and news terms should be ok in most situations.
Get an overview of the translation system configuration
It can be a daunting task to review translation status per content type. Fortunately, a complete overview of the configuration of fields per entity type is available here : /admin/config/regional/content-language
Entity reference translation
Entity references are defined via fields.
Example: an Article content type can reference an Article Type taxonomy term. Or an Article can reference an Organization content type.
Most of the time, you will not need to translate references, the only reason is to define different values per language.
Direction in Entity Relationships
Let's take a current use case: you want make a reference between two content types: Article and an Organization, to denote that the organization is the original author of the publication.
Basically, you have two options
- Define an Organization field in the Article content type
- Define an Article entity reference field in the Organization content type
First solution
Pros: Easy rendering and filtering. You will probably have less Organizations than Articles so you can expose your field via ...
Cons: Ordering should be defined by weight.
Second solution
Pros: Ordering can be done via drag and drop.
Cons: You will probably have more Articles than Organizations, so you will need to expose the field via autocomplete.
Changing the multiplicity of a field
Event if you have this warning, you can still change the multiplicity when data are defined for the field.
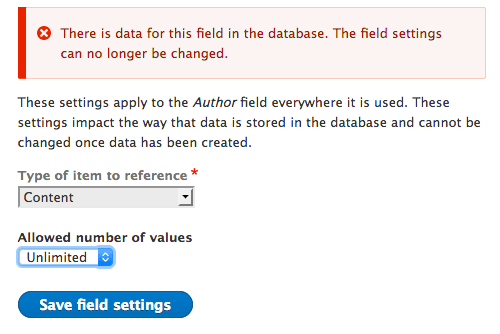
Be aware that multiplicity is shared among field instances.
Example: you have a Tags field (field_tags) that is defined on the Article content type with a multiplicity (number of values) of unlimited.
You define a new content type Event and share this field_tags. Then you define the multiplicity to 1 value. The side effect is that the Tags field has now one single possible value as well.
Note that other settings are not shared among field instances.
Example: for an image field, you can define different files directory for the storage.
This section needs to be completed
- Content translation
- Field dynamic values
- Multiplicity and compound fields